Lesson 4: Impact of materials on the environment
In this lesson, we will explore the environmental impact of materials used in various products and industries.
- Toxicity of Materials
- The production of materials often involves the use of approximately 30,000 anthropogenic chemicals, some of which have had devastating effects. A notable example is the Bhopal disaster in 1984, where methyl isocyanate killed thousands of people and affected many more. Additionally, Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs), DDT, PCBs, asbestos, and various other hazardous chemicals and materials have raised concerns.
- RoHS Directive
- The RoHS directive (Restriction of the use of certain Hazardous Substances in electrical and electronic equipment – 2002/95/EC) prohibits specific hazardous substances in electronic equipment, including mercury (Hg), lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), hexavalent chromium (Cr6+), polybrominated biphenyls (PBB), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE).
- Materials Prohibited/Restricted in the European Union
- The European Union restricts or prohibits certain materials due to their harmful effects. These materials include benzene, asbestos, polychlorine biphenyls (PCBs), carcinogens, lead compounds, mercury, arsenic compounds, cadmium, and others.
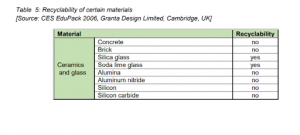
- Materials from the Aspect of Recyclability
- Material selection is a crucial aspect of product design. Designers aim to reduce waste, avoid toxic materials, and use resources efficiently. Recycling, reusing materials and components, and simplifying product design are essential strategies.
- Eco Processes
- Design and processes play a pivotal role in product lifecycles. Designers can apply measures like the DfX approach and the use of “SMART” materials to facilitate reprocessing and recycling. Clean technologies are crucial for designing eco-friendly products.
- Ecological Processes and Clean Technologies
- Manufacturing processes are closely linked to material selection and design quality. Clean technological processes aim to minimize waste generation, toxic emissions, and energy consumption throughout the product lifecycle.
Conclusion
- Understanding the environmental impact of materials is essential for creating sustainable and eco-friendly products. Designers and industries must prioritize materials that are safe, recyclable, and energy-efficient to minimize their ecological footprint.
In this lesson, we’ve explored how the choice of materials can have a significant impact on the environment. Recognizing the importance of using eco-friendly materials and clean technologies is crucial for reducing environmental harm and promoting sustainability.