Lesson 7: HEV, PHEV – division of hybrid vehicles in relation to their functions and driving modes
In this lesson, we’ll explore the different functions and driving modes of hybrid electric vehicles (HEV) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV), categorized by their hybridization levels. Additionally, we’ll delve into examples of well-known hybrid vehicles.
- Division of Hybrid Vehicles in Relation to Their Functions and Driving Modes (Hybridization Levels)
Hybrid electric vehicles come in various configurations, offering different functions and driving modes to optimize efficiency and reduce emissions. Let’s explore these modes:
1.1 Start/Stop Function
- The Start/Stop Function shuts down the internal combustion engine (IC engine) when the vehicle is stationary (e.g., at a red light).
- An electric motor quickly restarts the IC engine with optimal speed, powered by a rechargeable battery.
- The electric motor may also provide power to vehicle accessories while the IC engine is off.
1.2 Regenerative Braking Mode
- Regenerative braking captures kinetic energy during deceleration.
- An electric motor switches to generator mode, driven by the vehicle’s wheels, converting kinetic energy into electricity.
- This mode reduces the reliance on traditional hydraulic brakes, saving energy.
1.3 Hybrid Motion Mode
- In this mode, both the IC engine and the electric motor work together to provide the necessary torque for propulsion.
- Part of the IC engine’s torque may be used to start a generator and produce electricity for the electric motor or to charge the battery.
1.4 Movement Using Electricity Only (Electric Mode)
- The vehicle operates exclusively on electric power, drawing energy from the battery.
- The IC engine remains inactive, resulting in zero exhaust emissions and reduced noise levels.
- Ideal for short trips and urban driving.
1.5 Function of Battery Recharge at Charging Points (PHEV)
- Some hybrid vehicles can connect to the power grid for battery recharging.
- These are known as plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV).
- PHEVs offer extended electric-only driving ranges, making them versatile choices.
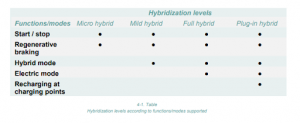
1.6 Division According to Hybridization Levels
- Hybrid vehicles are categorized by the level of hybridization based on their functions and driving modes.
- Fuel savings increase with higher hybridization levels, with PHEVs achieving the greatest savings.
- Examples of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
2.1 Toyota Prius
- The Toyota Prius is one of the most popular hybrid electric vehicles.
- Since its inception in 1997, over six million vehicles across four generations have been produced.
- Toyota’s Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD) system combines an IC engine with an electric motor for efficient performance.
2.2 VW Golf GTE/Audi A3 Sportback e-tron
- The VW Group introduced the VW Golf GTE and Audi A3 Sportback e-tron models to reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
- These plug-in hybrids feature a parallel configuration with a petrol engine and an electric motor.
- They offer options for electric-only driving and increased power when both engines work together.
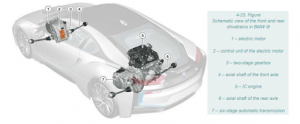
2.3 BMW i8
- The BMW i8 is a high-performance sports hybrid vehicle.
- It employs a unique configuration with both electric and IC engines driving different axles.
- The vehicle offers various driving modes for agility and economy, with a focus on electric-only driving in urban areas.
Conclusion
- Hybrid electric vehicles come in various configurations, offering different functions and driving modes.
- Examples like the Toyota Prius, VW Golf GTE/Audi A3 Sportback e-tron, and BMW i8 showcase the versatility and innovation in hybrid vehicle technology.
In this lesson, you’ve gained an understanding of the functions, driving modes, and examples of hybrid electric vehicles. The versatility of these vehicles makes them a crucial part of the automotive industry’s efforts to reduce emissions and improve efficiency.