Lesson 4: Fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV)
In this lesson, we will explore Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs), a remarkable category of electric vehicles that utilize hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity. We’ll delve into the technology behind fuel cells, their types, and examples of FCEVs available in the market.
- Introduction to FCEVs
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) are a unique class of electric vehicles powered entirely by electricity.
- Unlike battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) that store electricity in batteries, FCEVs generate electricity on the go using hydrogen fuel cells.
- FCEVs produce no exhaust emissions during operation, making them environmentally friendly.
- Fuel Cells
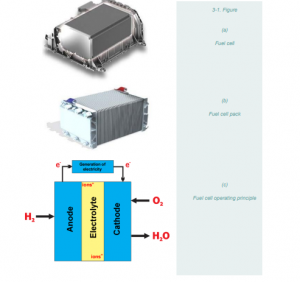
- Fuel cell technology is at the heart of FCEVs. It converts chemical energy into electrical energy through a chemical reaction.
- Fuel cells require a continuous supply of fuel (hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (usually oxygen from the air) to sustain the chemical reaction and produce electricity.
2.1 Structure and Operation of Fuel Cells
- Fuel cells consist of cathodes, anodes, and an electrolyte that allows positively charged hydrogen ions (protons) to move within the cell.
- A catalyst in the cathode and anode initiates the fuel reaction, generating positively charged ions and electrons.
- Hydrogen ions move through the electrolyte while electrons flow through an external circuit, creating a direct current.
- Fuel cells can be connected in series or parallel, depending on voltage and power requirements.
- They produce electricity, water, heat, and small amounts of other emissions depending on the fuel used.
- Fuel cell energy efficiency ranges from 40% to 60% and can increase to 80% with cogeneration (heat utilization).
2.2 Types of Fuel Cells
- Five main types of fuel cells are categorized based on their electrolyte type and operating temperature:
- Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC)
- Alkaline Fuel Cells (AFC)
- Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells (PAFC)
- Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFC)
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC)
- PEM Fuel Cells
- PEMFCs are a popular choice for hydrogen-powered vehicles due to their low operating temperature, enabling mobility.
- PEM fuel cells consist of a proton-permeable membrane, platinum electrodes, Teflon seals, and collectors.
- They efficiently convert hydrogen into electricity with a theoretical efficiency of approximately 83%.
- Examples of Fuel Cell Vehicles
- Various manufacturers have introduced FCEVs, demonstrating their commitment to this technology.
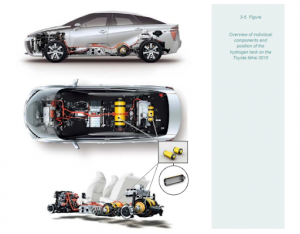
4.1 Toyota Mirai
- Toyota’s Mirai, launched in 2014, is a notable FCEV that uses PEM fuel cells.
- It features 370 cells in the fuel cell stack, offering a power output of 114 kW.
- Mirai’s hydrogen tank can be refilled in 3-5 minutes and provides a range of nearly 500 km.
4.2 Honda Clarity
- Honda’s Clarity, introduced in 2008, employs fuel cells with a power output of 100 kW.
- It can travel up to 372 km on a full hydrogen tank and features a lithium-ion battery.
4.3 General Motors HydroGen4
- General Motors produced the HydroGen4, based on the Chevrolet Equinox, from 2008 to 2010.
- It had a fuel cell power output of 93 kW and a 35 kW nickel-metal-hydride battery.
4.4 Hyundai ix35
- Hyundai’s ix35, released in 2012, achieved speeds of up to 160 km/h with a fuel cell power output of 100 kW.
- It boasted a projected range of 588 km with its type IV hydrogen tank.
- Challenges and Future Prospects
- Although FCEVs have made progress, mass production and commercialization are expected to take 15-20 more years.
- Various challenges, including fuel infrastructure and cost, need to be overcome.
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles represent a promising avenue for sustainable transportation, utilizing advanced technology to reduce environmental impact. Understanding their operation and provided examples offers insight into the future of clean energy mobility.
Conclusion
- FCEVs represent a unique and promising segment of electric vehicles, utilizing hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity.
- Different types of fuel cells exist, each with its advantages and limitations.
- Toyota, Honda, General Motors, and Hyundai are among the manufacturers exploring FCEV technology.
- Although FCEVs offer a sustainable and eco-friendly option, mass production challenges are expected to persist for several years.
In this lesson, you’ve explored the fascinating world of Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs), understanding their technology, construction, and real-world examples. These vehicles offer a greener alternative for sustainable transportation, driven by the power of hydrogen fuel cells.