Lesson 8: Autonomous vehicles and the automotive supply chain
In this lesson, we’ll explore the impact of autonomous vehicles (AVs) on the automotive supply chain, the emergence of new players, and the implications for suppliers.
- The Drive Toward Autonomous Vehicles
- Investment in autonomous vehicle (AV) development is driven by the potential for massive opportunities.
- Automakers aim to gain control over future costs and secure a share of the industry profit.
- AVs are expected to bring new business models to the transportation sector.
- New Links in the Value Chain
- The automotive ecosystem is evolving with the emergence of new players, including EV system makers, battery manufacturers, sensor technology providers, and AV software developers.
- Auto companies are tempted to expand into these areas, but it can lead to misallocation of resources.
- Success at different points in the value chain requires distinct capabilities.
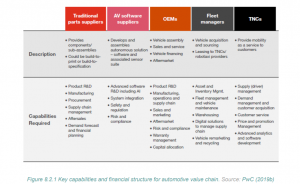
- Different Players in the Value Chain
- Traditional auto suppliers are asset-heavy, capital-intensive, and integrated into global supply chains.
- AV software suppliers are young companies with minimal physical assets but deep technical expertise.
- OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) have global manufacturing, R&D, and complex supply chains.
- Fleet managers will play a crucial role in AV adoption by maintaining expensive AV fleets.
- Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) will provide AV-enabled ride-hailing services.
- Implications for Suppliers
- Suppliers may need to adapt to new industry dynamics and competition.
- Offering different delivery models, from hardware solutions to integrated hardware-software solutions, can be beneficial.
- Access to fleet data is critical for developing advanced autonomous driving (AD) systems.
- Market dynamics may result in a “winner takes most” scenario for AD system suppliers.
- Succeeding in the Passenger Car Market
- Winning in the autonomous passenger car market requires a shift in R&D toward software-driven development.
- Fleet data utilization and flexible offerings for varying consumer price points are essential.
- Decoupling hardware and software development can reduce design costs.
- Customer-centric go-to-market strategies and exploring ownership models are key to success.
Conclusion:
- AV Investment Drivers: Investment in autonomous vehicles (AVs) is propelled by the potential for tapping into a significant market opportunity and securing a foothold in an evolving industry landscape.
- New Players Emerge: The automotive supply chain is witnessing the emergence of new players, including EV system makers, battery manufacturers, sensor technology providers, and AV software developers.
- Implications for Suppliers: Suppliers must adapt to new industry dynamics, potentially consolidating their offerings and exploring different delivery models. Access to substantial fleet data, funding, and talent will be crucial for success in the AV industry.
- Redefining Passenger Car Market: Success in the autonomous passenger car market requires a shift in R&D toward software-driven development, flexible offerings for consumers, and customer-centric go-to-market strategies.
- Strategic Considerations: Companies in the automotive sector must carefully evaluate their role in the value chain, balancing their existing strengths with their ambitions in new areas. Strategic decision-making will be vital in navigating the evolving AV landscape.
In this lesson, you’ve learned about the impact of autonomous vehicles on the automotive supply chain, the emergence of new players, and the challenges and opportunities for suppliers, OEMs, and other stakeholders in the evolving automotive industry. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for anyone involved in the automotive sector as it undergoes significant transformation due to the rise of autonomous vehicles.