Lesson 6 – ORGANISATION OF THE EXCHANGE OF INFORMATION
Lesson Overview: In this lesson, we will explore the organization and processes involved in the exchange of information for the development and review of Best Available Techniques (BAT) Reference Documents (BREFs) under Directive 2010/75/EU on Industrial Emissions. Learners will understand the roles of different stakeholders, including the European IPPC Bureau, the Forum, the Technical Working Groups (TWGs), and the Committee, in ensuring an effective, active, and transparent exchange of information to produce high-quality BREFs. The lesson will also cover practical arrangements for information exchange and the validation of BAT conclusions by the Committee.
Lesson Objectives: By the end of this lesson, learners will be able to:
- Describe the roles of the European IPPC Bureau, the Forum, and the TWGs in the exchange of information for BREFs.
- Understand the process of information exchange and its significance in producing high-quality BREFs.
- Explain the role of the Committee in the adoption of decisions on BAT conclusions.
Lesson Content:
- Introduction to the Exchange of Information
The exchange of information is a critical process in the development and review of Best Available Techniques (BAT) Reference Documents (BREFs) under Directive 2010/75/EU on Industrial Emissions. It involves various stakeholders collaborating to ensure a comprehensive and transparent exchange of data and knowledge.
2. The Role of the European IPPC Bureau (EIPPCB)
The European IPPC Bureau (EIPPCB), located in Seville, Spain, plays a central coordinating role in the information exchange process. The EIPPCB ensures that information is collected and processed according to the guidance provided and leads the work of the Technical Working Groups (TWGs) for each BREF.
3. The Role of the Forum
The Forum, established under Article 13 of Directive 2010/75/EU, is an expert group convened and chaired by the Commission. It includes representatives from Member States, relevant industries, and non-governmental organizations promoting environmental protection. The Forum ensures an effective and transparent exchange of information resulting in high-quality BREFs.
4. The Role of the Technical Working Groups (TWGs)
The TWGs are the main sources of information for the drawing up and reviewing of BREFs. They consist of active members from different stakeholders who actively collect and deliver information according to agreed deadlines. TWG members are responsible for reporting back to their respective Forum representatives if any issues arise during the information exchange.
5. The Role of the Committee
The Committee, consisting of representatives from all Member States, assists the Commission in implementing Directive 2010/75/EU. It is involved in the adoption of decisions on BAT conclusions resulting from the exchange of information.
6. Practical Arrangements for Information Exchange
Practical arrangements for the information exchange are laid down in Commission Implementing Decision 2012/119/EU. The exchange of data and information is facilitated through the use of the web-based software application called BATIS, which allows members to upload relevant information for the BREF development and review.
7. Validation and Publication of BAT Conclusions
Once the BREFs are finalized, the European IPPC Bureau presents each BREF to the Forum for validation. The BAT conclusions, validated by the Forum, are then presented to the Committee for adoption. Upon validation by the Committee, the BAT conclusions are published as Implementing Decisions in the Official Journal of the European Union.
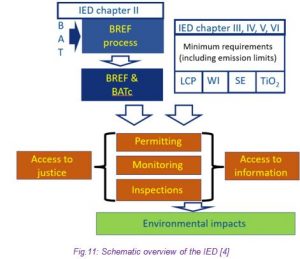
Conclusion:
The organization of the exchange of information involving various stakeholders, including the European IPPC Bureau, the Forum, the TWGs, and the Committee, is crucial in producing high-quality Best Available Techniques Reference Documents. This process ensures transparency, collaboration, and the use of scientific knowledge to promote environmental protection and sustainable industrial practices.