Lesson 4 – BAT Reference Documents (BREFs) and Guidance Material
Lesson Overview: In this lesson, we will explore the importance of Best Available Techniques Reference Documents (BREFs) and their role in promoting sustainable practices across various industries. We will learn how BREFs are developed through an exchange process and how they define activities, emissions levels, and consumption while focusing on the application of Best Available Techniques (BAT). Additionally, we will discuss the availability of BREFs in different countries and the related advisory material from various judicatures.
Lesson Objectives: By the end of this lesson, learners will be able to:
- Understand the significance of BAT Reference Documents (BREFs) in setting industry standards.
- Identify the industries covered by BREFs in the European Union.
- Recognize the availability of BREFs and guidance material in different countries.
Lesson Content:
- BAT Reference Documents (BREFs) and Their Purpose
BREFs are comprehensive reference documents that result from exchanges conducted in accordance with Article 13 of the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED). They are developed to define activities, current emissions levels, and consumption patterns while providing detailed descriptions of the application of Best Available Techniques (BAT). These documents play a crucial role in guiding industries towards environmentally friendly and efficient practices.
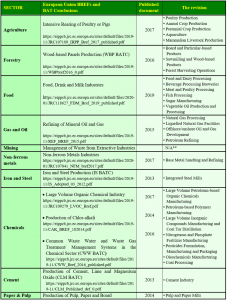
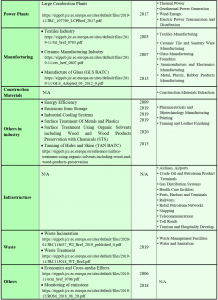
List of BAT BREF documents by sectors and activities
2. Industries Covered by BREFs in the European Union
The IPKZ European Office has approved 33 BREF documents for various industries. Some of the industries covered include:
- Pulp and paper production
- Iron and steel production
- Cement and lime production
- Refrigeration systems
- Chlorine and alkali production
- Ferrous metal processing
- Non-ferrous metal processing
- Glass production
- Leather processing
- Mineral oil and gas refineries
- Large-scale production of organic chemicals
- Waste water and waste gas management in the chemical industry
- Textile processing
- Monitoring systems
- Intensive pig and poultry farming
- Slaughterhouses and facilities for disposal or recovery of animals and animal waste
- Forges and foundries
3. Availability of BREFs and Guidance Material in Different Countries
BREFs and related advisory material vary across different countries. For the purposes of this lesson, we will focus on the BREFs available in the European Union. However, it is essential to note that other countries, such as the Russian Federation, Korea, the United States, the People’s Republic of China, and India, also have their own sets of BREFs and guidance documents.
Conclusion:
BAT Reference Documents (BREFs) play a vital role in promoting sustainable and environmentally friendly practices in various industries. By providing comprehensive information on Best Available Techniques (BAT) and their application, BREFs guide industries towards effective emission reduction and environmental protection. It is important for industries and policymakers to refer to these documents and stay updated with the latest developments and guidance material to ensure responsible and compliant operations. For more specific BREFs and guidance in different countries, learners are encouraged to explore the respective official sources and websites provided in this lesson.
BREFs are only guidance documents. They do not have legal status, their use is to guide Member States, industry, and the public on feasible emissions and consumption when using specified BAT techniques. When determining emission limits and other conditions, local conditions are always taken into account. The emission limit values may be lower or higher in specific cases. Air quality and environmental water standards may mean more stringent values – or possibly zero emissions/discharges. There may be cases where the emission limit values might be less stringent – aligned with the “best for the environment as a whole” principle, as it is stated by the source.