Lesson 1 – Maintenance and Organisation
In this lesson, we explore the essential concepts and functions of maintenance, covering its significance in ensuring the efficient operation of machinery and equipment.
The Evolution of Maintenance
- Today’s understanding of maintenance encompasses factors from construction to scrapping that influence machinery and equipment’s availability.
- The traditional terms like ‘maintenance,’ ‘repair,’ and ‘overhaul’ have been expanded to include concepts such as complex maintenance, comprehensive preventive maintenance, and terotechnology.
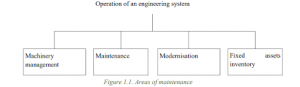
Terotechnology: A Holistic Approach
- Terotechnology is a cyclical process that encompasses various stages, including design, manufacture, installation, operation, maintenance, preservation, administration, and management of machinery and equipment.
- It forms the basis for managing fixed assets, maintenance, maintenance management, and level maintenance, ensuring a comprehensive approach.
The Concept and Function of Maintenance
- Industrial enterprises aim to transform low-value inputs into valuable products efficiently. This requires various activities, including marketing, design, production, and maintenance.
- Maintenance ensures that machinery and equipment remain in good working order, addressing wear and tear and the need for repairs.
Maintenance Activities
- Maintenance resources are crucial for operating machines safely and efficiently, aligning with safety standards and maximizing production with optimal use of resources.
- Developing a maintenance strategy aims to balance production and maintenance expenditure effectively, from preventive maintenance to exclusive breakdown maintenance.
Maintenance in Production
- Maintenance applies to both producers and users of machinery and equipment. It ensures that production is carried out with the required quality while equipment remains in good working order.
- The evolution of maintenance must align with the progress of production processes to achieve scientific and technical advancements.
The Concept and Task of Maintenance
- Maintenance focuses on installations, buildings, machines, and various material assets. It involves all operations to ensure serviceability and proper use, including care, cleaning, lubrication, and more.
- Maintenance aims to maintain the original utility value, restore equipment to the original service life, and, in some cases, increase the original service life.
Maintenance Operations
- Maintenance tasks can be continuous (e.g., cleaning, lubrication) or intermittent (e.g., repairs). Both are vital and have well-established systems for implementation.
- The DIN definition of maintenance emphasizes measures to preserve, restore, and maintain plant condition, aligning maintenance goals with business objectives.
The Role of Maintenance in Decision Making
- Maintenance is a critical part of decision-making throughout a machine’s life cycle, from its installation to scrapping.
- Choices made during maintenance significantly impact a machine’s cost-effectiveness and performance.
Machine Scrapping
- Eventually, due to wear, technical obsolescence, or economic considerations, machines reach a point where maintenance is no longer economical.
- When machines fail, the decision to repair or replace involves weighing factors like cost, downtime, and urgency.
The Lifecycle of Machine Parts
- During maintenance, machine parts may be repaired or replaced. Reconditioning technologies have emerged, offering a wide range of methods to restore degraded parts.
- Decisions about repairing machines often involve considerations of technical and economic factors.
Product Aftercare
- After selling their products, companies engage in aftercare activities such as warranty service, spare parts supply, and maintenance.
- Aftercare ensures that customers receive support and maintenance, enhancing the overall product experience.
Conclusion
- Maintenance is a comprehensive process that spans from the inception of machinery to its scrapping.
- Understanding the various stages of maintenance and their significance is crucial for efficient and cost-effective machinery operation.
Read the textbook from the 1st page. You can find the textbooks’s content on this link.