Lesson 7 Automotive Artificial Intelligence
Automotive Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is one of the most progressive technologies in computer science. It is associated with human intelligence through similar characteristics such as language understanding, reasoning, learning, problem-solving, and others.
Manufacturers in the market witness enormous underlying intellectual challenges in the development and revision of the technology. In addition, the growth in automotive industry is expected to drive the automotive artificial-intelligence market.
The automotive industry has experienced the promise of artificial intelligence and is among the major industries using AI to augment and mimic the action of humans. Furthermore, the emergence of standards such as advanced driver assistance system (ADAS), adaptive cruise control (ACC), blind spot alert, and growth in demand for convenience features attract automotive vendors towards AI [[i]].
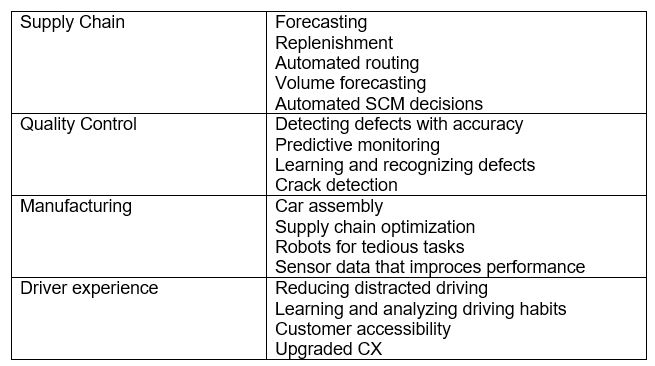
Table 7.1_AI in Automotive: Innovative Use Cases
AI-powered Vehicle prototyping
Like any other industry, the automotive industry suffers from cut-throat competition that necessitates rapid prototyping. But creating rapid prototypes that are not functional would not be feasible for car manufacturers. The new-age AI-powered prototyping uses innovative product development processes that eliminate several pain points present in the traditional prototyping and streamlines the entire process.
The usage of AI enables better CAD rendering and improves the prefabrication efficiency. In addition, it also helps enhance the quality of the product by allowing ML to point out design anomalies while supercharging the simulation process. In addition, artificial intelligence also helps automate repetitive tasks, enabling designers to focus on the more critical tasks [[ii]].
Monitoring Emissions.
With the AQI (Air Quality Index) of several cities in the world already beyond alarming levels, there is a drive to control or improve automotive emission levels and reduce the overall carbon footprint. AI and ML can lead to a major turnaround for the vehicle industry.
As per a BCG study, applying AI to corporate sustainability can increase savings and revenue to the tune of USD 1.3 trillion to USD 2.6 trillion by 2030 [[iii]].
Reduce carbon and costs with the power of AI
It would require vehicle companies to employ AI-powered data engineering that helps in automated emission tracking. It can also collect data from several operational activities throughout the value chain. It can also source data from other sources, such as satellites, layer them up to find missing data, and undertake meaningful emission monitoring actions.
The great strength of AI lies in its ability to learn by experience, collecting massive amounts of data from its environment, intuiting connections that humans fail to notice, and recommending appropriate actions on the basis of its conclusions. Companies looking to reduce their carbon footprint should turn the AI spotlight on all three components of the effort:
Companies can use AI-powered data engineering to automatically track emissions throughout their carbon footprint. They can arrange to collect data from operations, from activities such as corporate travel and IT equipment, and from every part of the value chain, including materials and components suppliers, transporters, and even downstream users of their products. AI can exploit data from new sources such as satellites.
By layering intelligence onto the data, AI can generate approximations of missing data and estimate the level of certainty of the results.
Predicting Emissions. Predictive AI can forecast future emissions across a company’s carbon footprint, in relation to current reduction efforts, new carbon reduction methodologies, and future demand. As a result, they can set, adjust, and achieve reduction targets more accurately.
Reducing Emissions. By providing detailed insight into every aspect of the value chain, prescriptive AI and optimization can improve efficiency in production, transportation, and elsewhere, thereby reducing carbon emissions and cutting costs.
AI in Manufacturing
AI tools can process and interpret vast volumes of data from the production floor to spot patterns, analyze and predict consumer behavior, detect anomalies in production processes in real-time, and more. These tools help manufacturers gain end-to-end visibility of all manufacturing operations in facilities across all geographies. Thanks to machine learning algorithms, AI-powered systems can also learn, adapt, and improve continuously.
Such capabilities are crucial for manufacturers to thrive in the aftermath of pandemic-induced rapid digitization.
Artificial intelligence in supply chain management
AI-enabled systems can help manufacturers assess various scenarios (in terms of time, cost, revenue) to improve last-mile deliveries. AI can predict optimal delivery routes, track driver performance in real-time, and assess weather and traffic reports besides historical data to forecast future delivery times accurately.
AI can also give manufacturers greater control over their supply chains from capacity planning to inventory tracking and management. They can set up a real-time and predictive supplier assessment and monitoring model to get notified the moment there’s a supplier failure and assess the extent of supply chain disruption immediately.
One example is that of the carmaker Rolls Royce. It uses advanced machine learning algorithms and image recognition to power its fleet of self-driving ships, which in turn improves its supply chain efficiency and safely transports its cargo.
McKinsey predicts that AI-enhanced supply chains will reduce:
- Forecasting errors by 20-50%
- Lost sales by 65%
- Over-stocking inventories by 20-50%
[i] StartUs Insight, Automotive Trend Report 2023 Automotive_Trend_Report_StartUs-Insights.pdf
[ii] https://www.birlasoft.com/articles/ai-use-cases-in-automotive-industry
[iii] https://www.bcg.com/publications/2021/ai-to-reduce-carbon-emissions