Lesson 3 – Eco-innovation of product – case of electric vehicles and working principles
Vehicles that do not require fossil fuels to operate and do not emit CO2 are major concerns for car manufacturers. The introduction of environmentally friendly technologies in the manufacturing chain aims to improve the functionality of cars, such as safety and comfort while reducing pollution and fuel consumption.
Different types of electric cars changed and are developed continuously giving users and potential users choices. Today the world is increasingly familiar with the terms BEV, HEV, PHEV and FCEV. How an electric vehicle works is depend on the type.
An electric car is a vehicle that is fully or partially propelled by electric motors, using energy stored in rechargeable batteries. The first practical electric cars were produced in the 1880s. Electric cars were popular in the late 19th century and early 20th century.
Innovation and advanced development in internal combustion engines (ICE) and mass production of cheaper gasoline vehicles has led to a decline in the use of electric vehicles.
The development of energy storage technology, especially battery technology, makes electric cars become more popular again at this time.
The Main Components of an Electric Vehicle
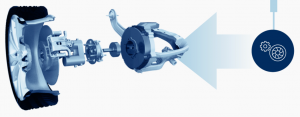
The electric vehicle drive system includes:
- High-voltage battery with control unit for battery regulation and charger
- Electric motor/generator with electronic control (power electronics) and cooling system
- Transmission including the differential
- Brake system
- High-voltage air conditioning for vehicle interior climate control
- Electric drive motors run quieter than internal-combustion engines. The noise emissions from electric vehicles is very low. At high speeds, the rolling noise from the tires is the loudest sound.
- Electric vehicles produce no harmful emissions or greenhouse gases while driving. If the high-voltage battery is charged from renewable energy sources, an electric vehicle can be run CO2 -free.
- In the near future, if particularly badly congested town centres are turned into zero-emissions zones, we will only be able to drive through them with high-voltage vehicles.
- The electric drive motor is very robust and requires little maintenance. It is only subject to minor mechanical wear.
- Electric drive motors have a high degree of efficiency of up to 96% compared with internal-combustion engines that have an efficiency of 35–40%.
- Electric drive motors have excellent torque and output characteristics. They develop maximum torque from standstill. This allows an electric vehicle to accelerate considerably faster than a vehicle with an internal combustion engine producing the same output.
- The drive train design is simpler because vehicle components like the transmission, clutch, mufflers, particulate filters, fuel tank, starter, alternator and spark plugs are not required.
- When the vehicle is braked, the motor can also be used as an alternator that produces electricity and charges the battery (regenerative braking).
- The high-voltage battery can be charged at home, in a car park and by using any accessible sockets. The blue charging connector on the vehicle and on public charging stations has been standardized across Germany and is used by all manufacturers.
- The energy is only supplied when the user needs it. Compared with conventional vehicles, the electric drive motor never runs when the vehicle stops at a red light. The electric drive motor is highly efficient particularly in lines and bumper-to-bumper traffic.
- Apart from the reduction gearbox on the electric drive motor, the electric vehicle does not require any lubricating oil.
Disadvantages of Electric Vehicles
- Electric vehicles have a limited range due to battery size and construction.
- Charging a high voltage battery can take a long time, depending on the battery charge and power source.
- The network of electric charging stations is sparse.
- If the destination is beyond the range of the electric vehicle, the driver will need to plan the journey. “Where can I charge my electric vehicle on the road?”
MOTOR’S GREEN TECHNOLOGY VEHICLE FROM HYUNDAI
Hyundai Motor has introduced several green technologies and developed green cars with the guidance of the ‘Blue Drive’ strategy. Hyundai Motor’s green models include a Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV), a Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) which can be charged using grid electricity, a zero-emissions battery Electric Vehicle (EV) and a Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) which is regarded as the ultimate green car.
Energy-efficient In-Wheel Motor
The in-wheel motor system enables an independent driving and braking with an electric motor equipped inside the wheel. It is a future-oriented, eco-friendly system that does not require an internal combustion engine, gearbox, or drive shaft. The motor and the brake are attached to each wheel, maximizing energy-efficiency and cabin space.
Figure_ The in-wheel motor system [https://tech.hyundaimotorgroup.com/article/ev-a-to-z-encyclopedia-tech-features]
Automakers in Germany, Japan, and the U.S. are also working on developing the system. Hyundai showcased its concept model with the in-wheel motor in it through the Hyundai N 2025 Gran Turismo design back in 2015. The system will be widely used in other electricity-powered, eco-friendly vehicles, such as FCEVs.