Lesson 9 – Value Chain Approaches to Determining BAT for Industry
Welcome to the lesson on Value Chain Approaches to Determining BAT for Industry! This course is designed to help you understand the importance of considering value chains in determining the Best Available Techniques (BAT) for industries to reduce their environmental impacts.
In today’s world, there is a growing need for industries to move towards a non-polluting, resource-efficient approach. To achieve this, value chains have shown the potential to deliver greater environmental benefits compared to less integrated approaches that focus only on individual stages. By taking a more holistic approach and accounting for the overall life-cycle impacts at the outset, we can identify practices that effectively consider an industry’s entire value chain to reduce environmental impacts.
This course is divided into different chapters that explore the various concepts that form the foundation of value chain approaches, such as green chemistry, resource efficiency, circular economy, and decarbonization. We will also assess overarching BAT policies and three sector examples, namely Textiles, Paints and Coatings, and Food Industries. By examining environmental issues associated with their value chains, we will see how upstream and downstream impacts from each sector impact the environment.
We will also discuss how regulatory bodies have responded to address value chain gaps arising from a sectorial/installation BAT approach by overlaying them with cross-cutting initiatives. By the end of the course, you will have a good understanding of how value chains can be incorporated into BAT determinations and related environmental regulatory and policy concepts.
So, let’s dive in and learn how value chain approaches can be used to determine BAT for the industry and achieve a more sustainable future!
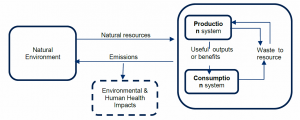
Illustration of the resource efficiency concept
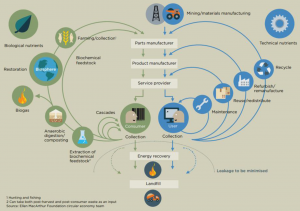
Illustration of the circular economy concept
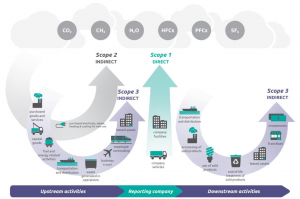
Overview of GHG protocol scopes and emission across the value chain
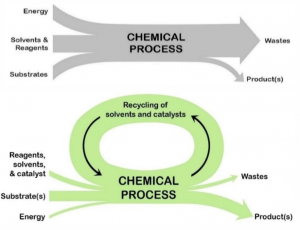
Green chemistry example